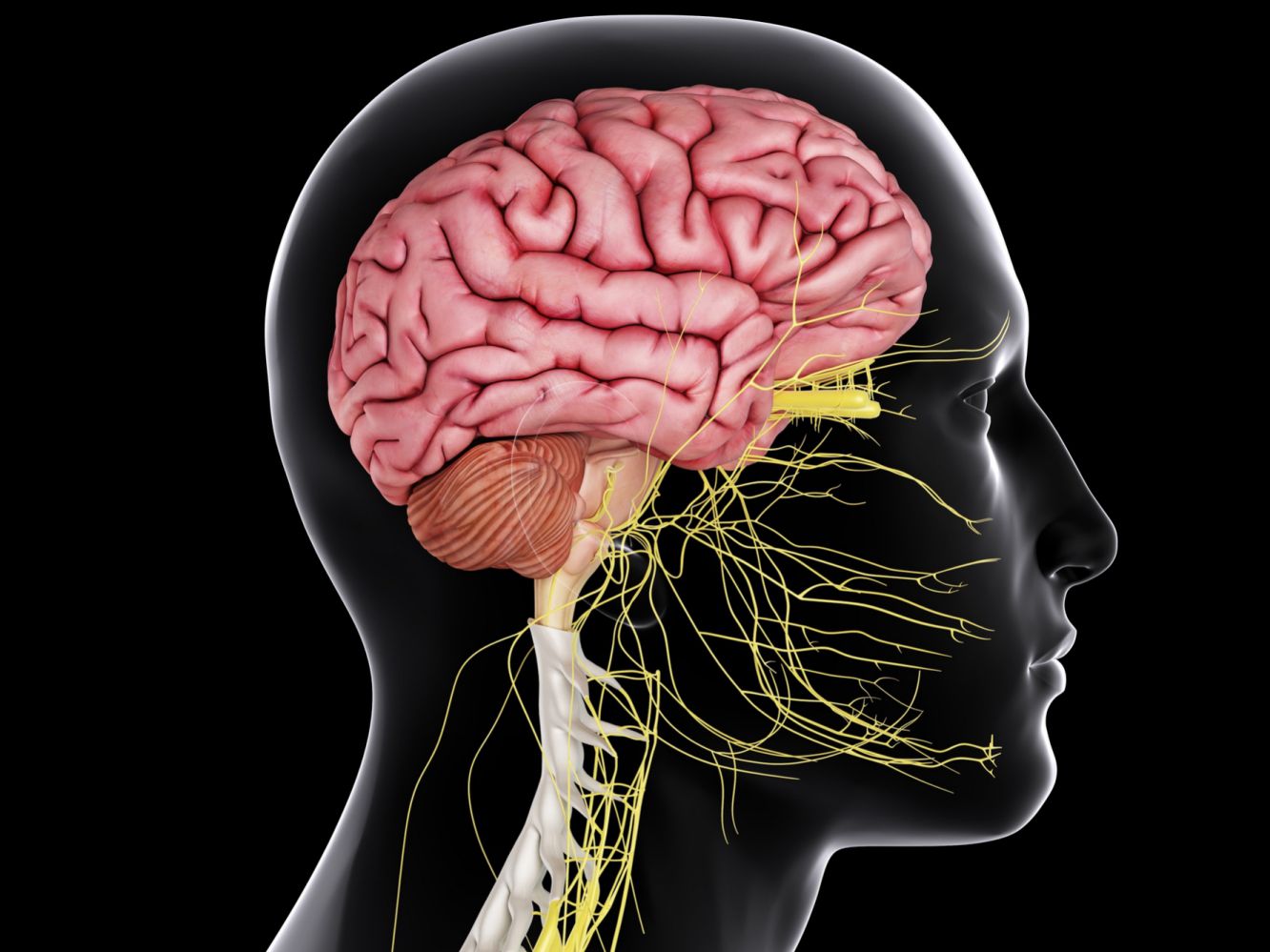
Nervous System ( Neurology) Head, Brain
Neurology is the branch of medicine concerned with the study and treatment of disorders of the nervous system
Headache
A headache can be a sign of stress or emotional distress, or it can result from a medical disorder, such as migraine or high blood pressure, anxiety, or depression.
Migraine
Migraine is a neurological condition that can cause multiple symptoms. It’s frequently characterized by intense, debilitating headaches.
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is sudden, severe facial pain. It’s often described as a sharp shooting pain or like having an electric shock in the jaw, teeth or gums.
Anxiety
Anxiety is your body’s natural response to stress. It’s a feeling of fear or apprehension about what’s to come.
Insanity
Insanity. n. mental illness of such a severe nature that a person cannot distinguish fantasy from reality, cannot conduct her/ his affairs due to psychosis, or is subject to uncontrollable impulsive behavior.
Melancholia
Biological psychiatrists understand melancholia as a severe mood disorder associated with dysfunctions along the body’s hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Epilepsy
A disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures.
Fits (Seizures)
A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain. It can cause changes in your behavior, movements or feelings, and in levels of consciousness.
Depression
A mental health disorder characterised by persistently depressed mood or loss of interest in activities, causing significant impairment in daily life.
Impulse
Impulse-control disorder (ICD) is a class of psychiatric disorders characterized by impulsivity failure to resist a temptation, an urge, or an impulse; or having the inability to not speak on a thought.
Neurasthenia
A condition that is characterized especially by physical and mental exhaustion usually with accompanying symptoms (such as headache and irritability), is of unknown cause but is often associated with depression or emotional stress.
Mental disorders
There are many different mental disorders, with different presentations. They are generally characterized by a combination of abnormal thoughts, perceptions, emotions, behaviour and relationships with others
Shock (Apoplexy)
apoplectic shock. An obsolete term for the depression of neurologic function which follows cerebral haemorrhage (stroke); it is little used in the working medical parlance
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some combination of hallucinations, delusions, and extremely disordered thinking and behavior that impairs daily functioning, and can be disabling
Brain Tumor (Benign/ Malignant)
Benign brain tumors are noncancerous. Malignant primary brain tumors are cancers that originate in the brain, typically grow faster than benign tumors, and aggressively invade surrounding tissue. cancer treatment depends on disease stages. Homeopathy treatment based on symptomatic as a holistic approach to cure diseases, this treatment is not a final treatment for you and take further treatment consult to your doctor
Lack of concentration
Difficulty concentrating is a normal and periodic occurrence for most people. Tiredness and emotional stress can cause concentration problems in most people.
Somatic disorders
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) occurs when a person feels extreme, exaggerated anxiety about physical symptoms. The person has such intense thoughts, feelings, and behaviors related to the symptoms, that they feel they cannot do some of the activities of daily life.
Hyperactive
A chronic condition including attention difficulty, hyperactivity and impulsiveness.
Phobia
A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. The phobia typically results in a rapid onset of fear and is present for more than six months.
Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or “a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect.”
Paralysis (Hemiplegia/ Paraplegia)
There are many different causes of paralysis -and each one may result in a different kind of paralysis, such as quadriplegia (paralysis of arms and legs), paraplegia (being paralyzed from the waist down), monoplegia (paralysis in one limb), or hemiplegia (being paralyzed on one side of the body).
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy is due to abnormal brain development, often before birth.
Nervous Breakdown
A nervous or mental breakdown is a term used to describe a period of intense mental distress. During this period, you’re unable to function in your everyday life.
Weakness
Asthenia, also known as weakness, is the feeling of body fatigue or tiredness. A person experiencing weakness may not be able to move a certain part of their body properly.
Brainfag
Brain fag (uncountable) A condition to which male high school and college students are prone consisting of difficulty in concentrating, mild forgetfulness, and difficulty in maintaining a train of thought, arising from too much thinking.
Memory problem
It’s the stuff movies are made of: After a blow to the head, a person wanders aimlessly, unable to remember who he is or where he came from. While such sudden, profound loss of memory is rare, memory loss is a problem that affects most people, to a degree
Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a rare disorder in which your blood doesn’t clot normally because it lacks sufficient blood-clotting proteins (clotting factors). If you have hemophilia, you may bleed for a longer time after an injury than you would if your blood clotted normally.
Neuralgia
Neuralgia is a stabbing, burning, and often severe pain due to an irritated or damaged nerve. The nerve may be anywhere in the body, and the damage may be caused by several things
Parkinson disease
Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinson’s disease is a brain disorder that leads to shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with walking, balance, and coordination.
Forgetfulness
Forgetfulness can be a normal part of aging. As people get older, changes occur in all parts of the body, including the brain.
Dementia
Dementia is a collective term used to describe various symptoms of cognitive decline, such as forgetfulness.
Mental Shock
Psychological shock is when you experience a surge of strong emotions and a corresponding physical reaction, in response to a (typically unexpected) stressful event.
Vertigo
Vertigo is the feeling that you’re moving when you’re not. Or it might feel like things around you are moving when they aren’t. Vertigo can feel similar to motion sickness. It may sign of chronic illness or neurologically.